Overview
What is neural audio autoencoder and why using latent terrain?
Last modified 2026-01-06
Jasper Shuoyang Zheng
A neural audio autoencoder (such as RAVE) is an AI audio generation tool, it has two components: an encoder and a decoder.
- The
encodercompresses a piece of audio signal into a sequence of latent vectors (a latent trajectory). This compression happens in the time domain, so that the sampling rate goes from 44100Hz (audio sampling rate) to 21.5Hz (latent space sampling rate). - The
decodertakes the latent trajectory to produce a piece of audio signal. The decoder can also be used as a parametric synthesiser by navigating the latent space (i.e., latent space walk).
A latent terrain is a surface map created from latent trajectories, see the screenshot below, it's like looking at a latent trajectory from above. A latent trajectory can be generated by pathing through the terrain surface. Therefore, sound synthesis is achieved by sampling across the terrain to produce latent trajectories, which are then passed through the decoder to reconstruct waveform.
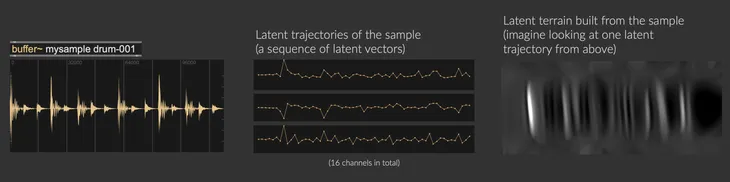
Latent terrain aims to be nonlinear (i.e., able to produce complex sequential patterns), continuous (i.e., allows for smooth interpolations), and tailorable (i.e., DIY your own materials with interactive machine learning).
You may have seen "latent space walk" animations created by AI image generators, for instance, this is a latent space walk in a diffusion transformer:

Credit: https://github.com/rnbwdsh/ComfyUI-LatentWalk
In parallel, this is an latent space walk with Music2Latent, and we're using the mouse (stylus) to control the sampling position in a terrain: